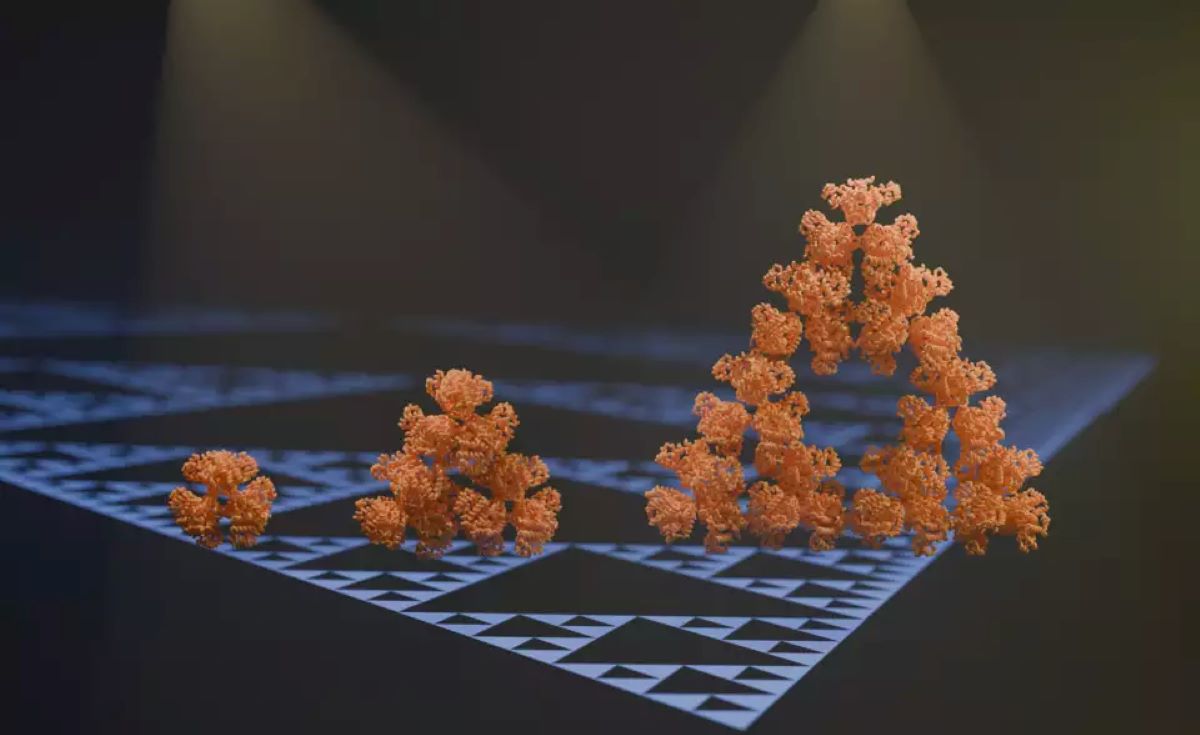
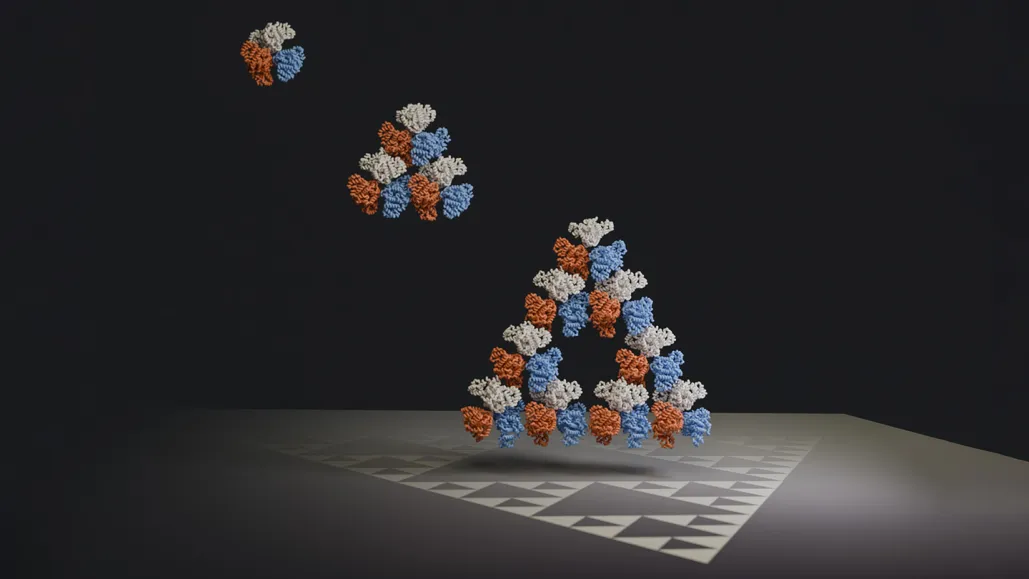
Scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery of a natural protein exhibiting self-similarity, forming a fractal—a mathematical pattern—never before observed at the molecular level. Fractals are intricate patterns that repeat on different scales, commonly found in nature but unprecedented in molecular structures until now. This finding challenges existing notions of self-assembly in nature and underscores the remarkable potential of molecular evolution.
The protein, identified as citrate synthase, originates from photosynthesizing bacteria and possesses a distinctive structure that enables it to spontaneously arrange into a unique fractal pattern.
Franziska Sendker, the lead author of the study, expressed astonishment at the discovery, emphasizing the unexpected nature of their observation using electron microscopy. The protein forms triangular shapes, with progressively larger voids emerging within them as the fractal grows, presenting a novel phenomenon in protein assembly.
Scientists Surprised by Unique Evolutionary Discovery (Credits: Science News)
Published in the journal Nature, the study describes how computer simulations vividly illustrate the protein’s self-assembly into an infinitely expanding pattern of triangles, marking the first observation of fractals at the molecular scale. Despite citrate synthase being a common microbial enzyme, this particular variant’s ability to form a fractal structure distinguishes it from other known forms, including those found in human cellular processes.
The evolutionary origins and significance of this peculiar fractal pattern remain enigmatic. While it is uncertain why the protein evolved to exhibit such a pattern, researchers speculate that its formation might have been accidental.
Experimentation involving genetically modified bacteria, which were unable to form the fractal structure, surprisingly demonstrated comparable growth rates under various conditions, suggesting the pattern may not confer any significant evolutionary advantage.
Georg Hochberg, an evolutionary biologist involved in the study, postulates that this molecular fractal might represent a fortuitous outcome of evolution, arising due to the ease of its construction rather than a selective advantage. This notion challenges traditional views of complexity in biological structures, suggesting that seemingly intricate patterns could emerge through evolution without a clear adaptive purpose.
The discovery of a molecular fractal emerging through evolutionary processes implies the existence of potentially undiscovered complex patterns in molecular biology. This revelation underscores the need for further exploration into the mechanisms and implications of such structures, which may offer new insights into the underlying principles of biological organization and evolution.